| What's MICA |
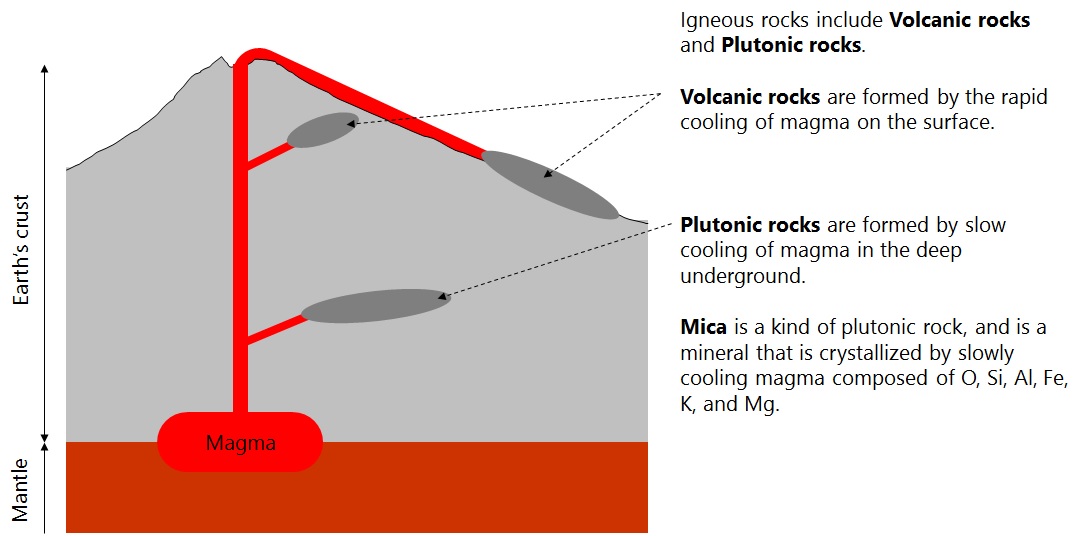 |
It says that 99% of elements in earth's crust is consist of O, Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Na, K, Mg in descending order of content.
Mica is one of the pyrocrystalline igneous rocks containing these elements in a specific ratio and is classified into
phyllosilicate. The basic structure of the phyllosilicate is based on interconnected
six member rings of SiO4 tetrahedra
that extend outward in infinite sheets. Three out of the 4 oxygens from each tetrahedra are shared with other tetrahedra.
Mica exist in the strata around the world. Its constituent elements and crystalline structure depend on the locality.
The photos below show muscovite and phlogopite. Recently, sythetic mica
has also been manufatured. |
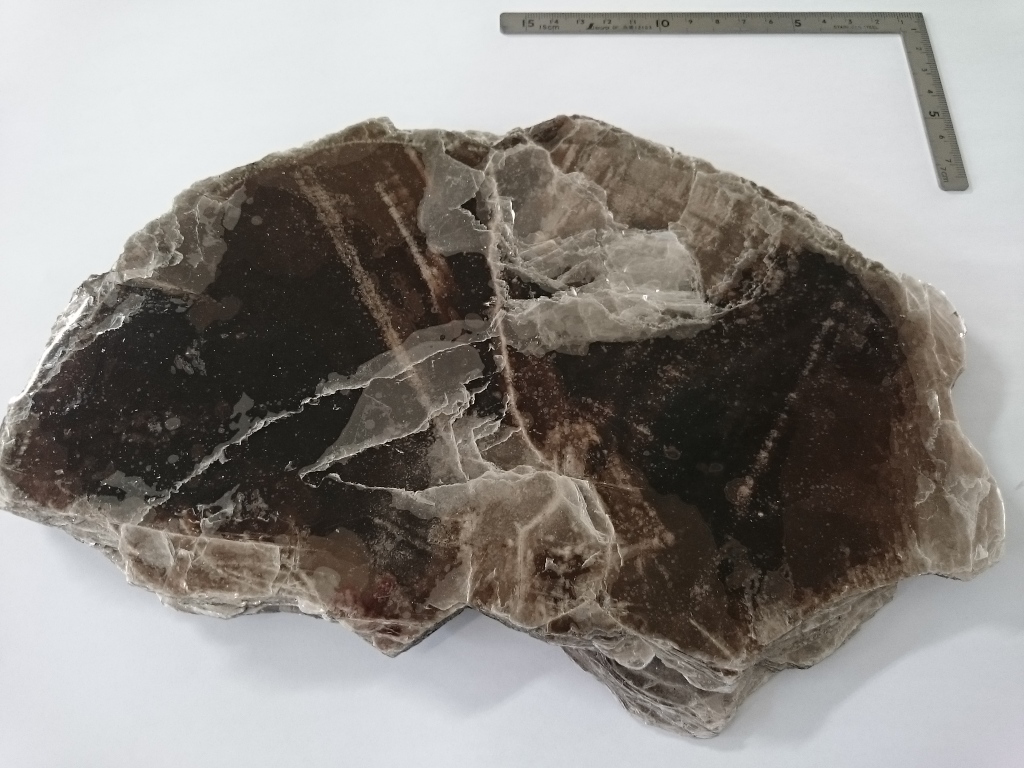

Raw ore of Indian Muscovite |
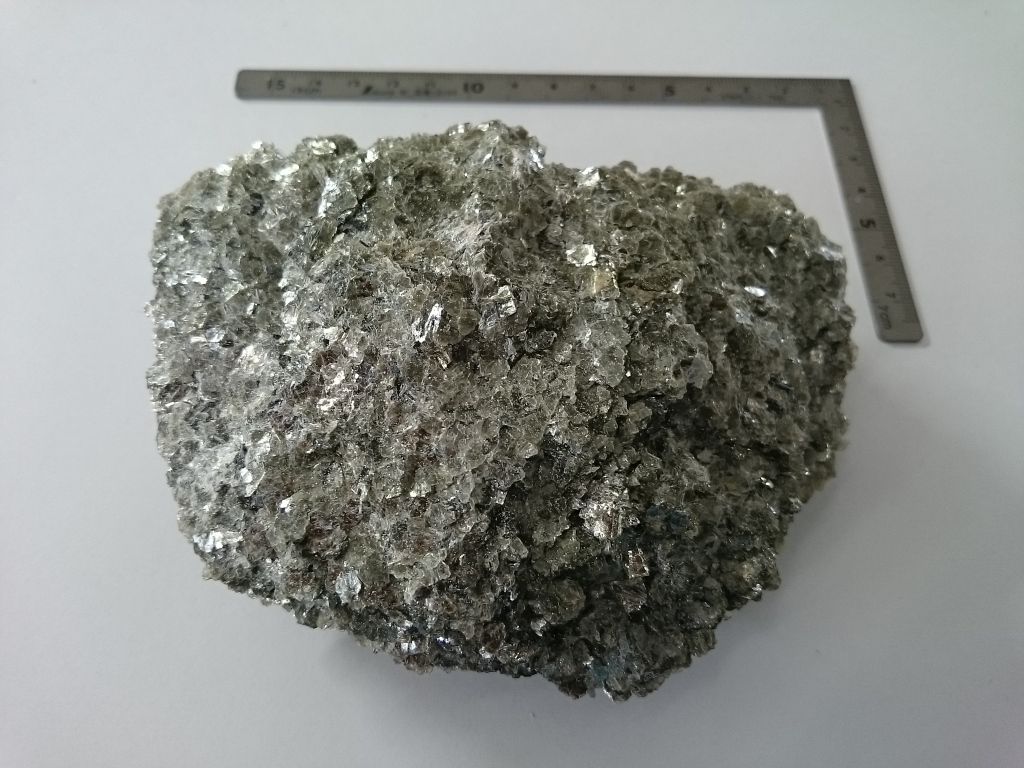

Raw ore of Chinese Muscovite |
The left photo is Indian muscovite ore and the right is Chinese muscovite
ore. Even in the same muscovite, the crystal
state is completely different, Indian ore has large crystals and good quality, and Chinese ore has small crystals and is
mixed with silica sand. The table below shows the details of major sheet
phyllosilicate |
| MICA TYPE |
Composition formula |
Characteristics |
| Muscovite |
KAl2(AlSi3)O10(OH)2 |
Rude ore is a brownish natural platy mineral.
Octahedral ions in a crystal are mostly occupied with Al. |
| Phlogopite |
KMg3(AlSi3)O10(OH)2 |
Phologopite is darker than muscovite and soft.
Octahedral ions in a crystal is mostly occupied with Mg. |
| Sericite |
KAl2(AlSi3)O10(OH)2 |
Rude ore is a greenish gray, natural platy mineral, same
composition as muscovite but its smaller crystals due to
hydrometamorphism |
| Synthetic Fluoro Phlogopite |
KMg3(AlSi3)O10F2 |
Synthetic fluorophlogopite, contains no (OH) of the natural
phlogopite instead the (OH)- is fully substituted with F.
White and a little rigid. |
|
|
|